Bulletin 155
September 2005 – Bulletin 155
Recusancy in Mitcham – J A Goodman & J Pile
Trafalgar 200 – J A Goodman
200 Years Ago (Nelson) Sept-Dec 1805 – J A Goodman
A Note on Nelson’s Gardener – J A Goodman
‘Hatfeild’s Park: the untold story’ – S Harris
Mitcham Cricket: an anthology – J A Goodman
and much more
PRESIDENT: J Scott McCracken BA FSA MIFA PRESIDENT: J Scott McCracken BA FSA MIFA
VICE PRESIDENTS: Viscountess Hanworth, Lionel Green and William Rudd
BULLETIN NO. 155CHAIRMAN: Peter Hopkins SEPTEMBER 2005
PROGRAMME SEPTEMBER.DECEMBER
Thursday 15 September 1.30 pm .Pubs of Merton (past and present).
A walk led by member Clive Whichelow, author of the book on the same subject.
Maximum 25. Please book with Sheila.
Meet outside the Leather Bottle, Kingston Road, opposite the Nelson Hospital. Bus routes
152, 163, 164, K5; short walk from Merton Park Tramlink stop or Wimbledon Chase station.
Wednesday 5 October 7.30 pm St Mary’s church, Merton
The Evelyn Jowett memorial lecture for 2005
.An appreciation of Vice Admiral Horatio Viscount Nelson, Duke of Bronte.
Pat and Ray Kilsby will present their illustrated tribute to a national hero .
his public career and his private life.
The church is in Church Path, Merton Park, a short walk from several bus routes, from
Wimbledon Chase station or from the Merton Park Tramlink stop.
Saturday 5 November 2.30pm Snuff Mill Environmental Centre
Annual General Meeting
After the business part of the meeting there will be a talk by member Desmond Bazley on
.Gunpowder, Treason and Plot..
To reach the Snuff Mill Centre from Morden Hall Garden Centre car-park cross the bridge
between the café and the garden centre, go through the gateway in the wall, turn right and
follow
the main pathway to the right, which leads to the Snuff Mill Centre. Numbers here are limited.
Morden Hall Road is on several bus routes and is close to Morden town centre.
Saturday 3 December 2.30pm St John’s Church Hall, High Path SW19
.Merton Priory . a Glimpse of Greatness’
Lionel Green, a founder member and a Vice-President of the Society, will talk on the
subject which he has been researching for more than half a century,
and of which he is the acknowledged expert.
High Path is off Morden Road SW19, which is served by several bus routes.
It is close to South Wimbledon station.
Parking is kindly being allowed at Merton Abbey Primary School opposite.
Note that there is no entry for cars to High Path from Morden Road.
The Society’s events are open to the general public, but visits must be booked.
You are invited to make a donation to help with the Society’s running costs.
.NELSON IN HIS OWN WORDS’
A Talk by Dr Colin White
At St Mary’s Church, Church Path, Merton Park SW19 on Monday 12 September at 8.00pm
Booking is now open to the general public.
Tickets cost £5.00 and Colin White’s book will be available at a discount.
RECUSANCY IN MITCHAM AND THE LOVELLS OF MERTON
Some further notes
Member JOHN PILE has written several times since the last Bulletin came out, with more
information he has
discovered about several recusant gentry families with links to Mitcham, and in one case to
Merton. He has also
drawn up some elegant family trees. I hope to include an article by him in the December issue.
He suspects that
the key factors in Mitcham’s role as a centre of recusancy were firstly a network of family
connections and
secondly Mitcham’s proximity to London. Meanwhile, here are some very brief notes from John’s
findings,
which add to the information in the June issue.
The Mitcham John Leedes (or Leeds) was a member of a Sussex family, lords of the manor of
Wappingthorn
in Steyning, whose estates appear to have been confiscated for recusancy in 1572, but later
restored. Leedes
was connected by marriage with John Caryll of Warnham, and one wonders whether this was the Sir
John
Caryll who bought the manor of Biggin and Tamworth in Mitcham from the Whitneys in 1603. Henry
Whitney’s
wife Anne was the daughter of Nicholas Saunder, a prominent recusant of Ewell. The Carylls were
a large and
widespread Roman Catholic family, mainly in Sussex and Hampshire. Sir John Caryll had links
with a Sir
Thomas Lovell of Norfolk, almost certainly of the same family asSir Gregory Lovell of Merton
Abbey, whose
father was Sir Francis Lovell of East Harling, Norfolk. And it is clear that even if Sir
Gregory himself conformed
there was a strong background of recusancy in his family. John Leedes also knew Sir Thomas
Tresham, as
they were imprisoned together for a time at Ely.
William .Tirwight. was probably a member of the Tyrwhitt family of Kettleby, Lincolnshire, who
were also
prominent recusants at the time. One of the Gunpowder Plot conspirators, Ambrose Rookwood, was
married to
Elizabeth Tyrwhitt, the daughter of William Tyrwhitt of Kettleby (c.1550-1591). Could this be
the William
Tirwight who turned up in Mitcham in 1589? Sir Robert Tyrwhitt leased some land in the manor of
Wimbledon,
and the family were connected by marriage with the Cecils, lords of that manor. The Lovells
also find a place in
the same family tree.
A Joan Rutland of Southwark was convicted of and fined for recusancy in 1588. Her surname is
not common,
and there may be a connection with Mitcham to be found.
John Pile is also interested in the possibility thatSir Julius Caesar of Mitcham, despite his
crown appointments,
mixed with recusants, and he cites Eric Montague’s article in Surrey Archaeological Collections
67, which
suggests that William Rutland of Colliers Wood and his friend Sir Gregory Lovell of Merton
Abbey were
frequent visitors at Caesar’s house.
And of course there is the case of John Donne. Though nominally a convert to Anglicanism, Donne
is thought
by many to have remained essentially Catholic in his private devotions. It would be worth
researching into
Donne’s family and friends. Was Mitcham a significant choice of retreat for him? JG
TRAFALGAR 200
.Nelson and his Times, as commemorated on Pub Signs. is a slide presentation by David Roe, one
of
our members. David is an avid collector of photographs of pub signs and is a member of the Inn
Sign
Society. He has given presentations to many local groups, including one to the Society, on the
history of
pub signs. This is an unusual and entertaining look at the depiction of pub signs of Lord
Nelson, the naval
and other events of his time, and the persons in his life, such as Lady Hamilton, and his
fellow officers.
Saturday 12 November 2.30pm. Committee Rooms, Merton Civic Centre (access via rear door
from car-park). Admission free, but names and number to be notified in advance to Merton
Heritage
Centre on 020 8640 9387 or heritage.centre@merton.gov.uk
MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY . BULLETIN 155 . SEPTEMBER 2005 . PAGE 2
TRAFALGAR 200
.The Trafalgar Way’
The Ordnance Survey have produced for the Trafalgar Bicentenary a special map which
commemorates
the journey made by Lieutenant John Richards Lapenotiere from Falmouth to the Admiralty in
London,
when he brought the news of Trafalgar. He travelled non-stop by post chaise, covering the 270
miles
(435km) in an impressive 37 hours, arriving at one o.clock in the morning of 6 November. Lord
Barham,
the First Lord, was roused from his bed to be told the news.
The map delineates Lapenotiere’s route, marks the places where he changed horses, and even
shows his
probable route street by street through some of the towns. It also picks out a few places with
a Nelson
connection near the route . Trafalgar Park, the Hardy monument and so on . and some with no
such
connection at all.
There is a brief account of the battle itself, but also, dismayingly, a sadly inaccurate piece
headed .Merton
Place/Morden Hall.. This refers to .Lady Emma Hamilton., instead of .Lady Hamilton. or .Lady
(Emma)
Hamilton.. And, while it correctly places Abraham Goldsmid at Morden Lodge it has him killing
himself
in the grounds of Merton Place, instead of, as he did, on his own property. Also it tells us
that Morden
Hall was built after Morden Lodge was pulled down: presumably the OS think that it was built on
the
site of Morden Lodge. In fact of course Morden Hall, built half a century before Goldsmid’s
Morden
Lodge, was nothing to do with either Goldsmid’s or Nelson’s property. Sir Robert and Lady
Burnett,
who lived at Morden Hall in Nelson’s time, are not recorded as even meeting either of their
distinguished
neighbours. And it is the present Morden Lodge that replaced Goldsmid’s house .
The map also shows what may have been Nelson’s route on his last journey to Portsmouth, on the
night
of 13/14 September 1805. I venture to disagree with the OS here. They have Nelson travelling
from
Merton to Kingston to pick up the Portsmouth road. This ignores the fact that Kingston Road was
a mere
parish road, poorly maintained. It would have represented five miles of rutted, possibly muddy,
track.
Nelson’s house was on the well-surfaced turnpike road to Epsom and beyond. I believe he would
have
taken this road, the present A24, as far as Leatherhead, and then the one, also turnpiked,
which is the
present A246 to Guildford, picking up the Portsmouth road. I can’t prove it, but surely speed
and comfort
would have been Nelson’s choice, and hang the expense!
Despite these remarks this interesting map is well worth having. It presents a lot of material
in a useful
and attractive form. It costs £6.25 and is available widely, and locally at the National Trust
shop at
Morden Hall Park.
JG
IN BRIEF
©
!!!!!.New Dawn Women. is the title of an exhibition at the Watts Gallery, Compton, near
Guildford, which is on
until 28 September, every day except Thursday from 2pm to 6pm, also Wednesday and Saturday from
11am
to 1pm. Women active in the Arts and Crafts and Suffrage movements are represented by a wide
range of
work . jewellery, embroidery, illustrating, book design, enamelling, including a number of
items made by
Ernestine Mills, pupil and biographer of Merton Park artist Frederic Shields. Tel: 01483 810235
©
!!!!!A computer-based virtual reality model of Nonsuch Palace is on display in the foyer of
Surrey History
Centre, 130 Goldsworth Road, Woking, until 19 November. Experience the amazing splendour of
Henry
VIII’s long-lost palace, recreated from contemporary paintings, manuscript descriptions and
archaeological
evidence. Admission free. Tuesdays & Wednesdays 9.30-5.30, Thursdays 9.30-7.30, Fridays 9.30-
5.00,
Saturdays (not 27 Aug) 9.30-4.00 (Closed Sundays & Mondays). Free parking, or bus from Woking
Station.
TRAFALGAR 200
Don’t forget the National Maritime Museum’s spectacular exhibition Nelson and Napoleon, which
is
on until 13 November. And it is worth crossing Romney Road afterwards to admire Benjamin West’s
1812 pediment sculpture of the death of Nelson. Made of Coade stone, it is in the King William
Court of
the old Naval College (now the University of Greenwich).
MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY . BULLETIN 155 . SEPTEMBER 2005 . PAGE 3
PLEASURE GARDENS OF CLERKENWELL
In warm weather on 26 May a group of the Society’s members forsook the south-western suburbs
for a much
less familiar part of London, to engage in a picturesque visit to the past. As part of a
Birkbeck College diploma,
Sheila Miller, one of our members, recently undertook a study of Clerkenwell’s spas and
pleasure gardens, and
we are fortunate that she offered to share with us some of her findings. She led us round a
circuit that took in
nine of the twelve gardens she believes to have flourished within or (in one case) just on the
borders of
Clerkenwell.
Before setting off, Sheila pointed out that our meeting point, at Angel underground station,
was on an old
drovers. road, along which stock destined for Smithfield would have been driven. The original
Angel would
have been one of many inns that catered for the thirsty drovers. Nearby, what is now
Pentonville Road was once
New Road, built in 1756 as part of London’s earliest bypass.
Sadlers Wells was our first stop, on busy Rosebery Avenue. Hard to believe, but the original
building once
fronted the New River, the artificial watercourse of the late 16th century that brought clean
water to London
from Hertfordshire. Here a Mr Sadler built a music house and laid out pretty gardens. In 1683
he rediscovered
an old well on the site, whose not unpleasant waters were faintly medicinal (they were said to
contain small
amounts of iron). In no time water-drinking, beer (brewed with the water), and acrobatic
displays were added to
the musical entertainment, and Sadlers Wells became famous. Not far into the next century
however the gardens
and the waters were no longer the attraction. Theatre and variety had taken over.
Inside today’s building we were able to see a collection of old prints of Mr Sadler’s
establishment, and a mock-
up of the old well.
Just across the road is a small park of
grass, shrubs and trees. Spa Green now
lies in the shadow of the Spa Green
Estate. It is the site of Islington Spa,
or New Tunbridge Wells, which
flourished from 1684 to as late as about
1820. It had the same chalybeate water
as Sadlers Wells (and Tunbridge Wells
itself) and offered its customers walks,
arbours, dancing, a long room and
lotteries. Its popularity waned early in
the 18th century, but revived for a time
under the patronage of Princesses
Amelia and Caroline, daughters of
George II.
In Amwell Street is New River Head, where the water from Myddelton’s New River was stored for
pumping
into London’s pipes. It is still an impressive site, though it no longer has a horse-pump or
even its six-sailed
wind-pump. Opposite once stood a tavern called Merlin’s Cave, where, between 1735 and early in
the next
century, Londoners could stroll in extensive gardens and play at skittles. The décor is thought
to have included
pictures of the magician.
Our route next took us past Lloyd Square of 1833 (.especially attractive
and complete. . Pevsner) and Granville Square, steeply down to Kings
Cross Road, where, across the road from us, a plaque marked the site of
Bagnigge Wells. These gardens straddled the Clerkenwell/St Pancras
border, formed here by the River Fleet, which was crossed by a rustic
bridge. Bagnigge’s heyday was from 1759 to about 1841, and at the
peak of its popularity patrons could enjoy dancing, organ music in the
long room, bowls and skittles, and teas (there was a bun house), as well
as the enticing charms of shady arbours and a grotto. Mr Hughes, the
first proprietor, was fortunate (or ingenious) in finding both chalybeate
and purging waters on his land. Many of the patrons were .Cits., self-
made merchants and tradesmen and their families. It is said that the
highwayman ‘sixteen-Strings Jack. was once thrown out of a window
here, only shortly before he was hanged at Tyburn. .Bagnigge. survives
as the name of a block of flats nearby.
Islington Spa in 1733, from W Wroth The London Pleasure Gardens of theEighteenth Century
MacMillan, London 1896
Bagnigge Wells, a contemporary print
MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY . BULLETIN 155 . SEPTEMBER 2005 . PAGE 4
Uphill again, to Exmouth Market, and the site of the Spa Fields Pantheon (1730-1776), which
replaced the
Ducking Pond House inn, and offered a teahouse and large gardens. There was also a statue of
Hercules. An
unpretentious place, it was frequented, mainly on Sundays, by servants and small tradespeople..
The building
later became a Nonconformist chapel, and the site is now occupied by the High Anglican church
of the Holy
Redeemer (.powerful . exceptional. . Pevsner).
The London Spa(w) (1685 – ?) and theEnglish Grotto (1760 – ?) more or less faced each other
where Rosoman
Street meets Skinner Street. Both probably closed towards the end of the 18th century. The
former had a chalybeate
spring, and the grotto of the latter was in a garden setting.
Across the small Spa Fields park, in the acute angle of Northampton Road, is the site of the
New Wells (1738
. 1750). Here visitors could loiter in yet another grotto, and there was a pond with goldfish,
a collection of wild
animals, an occasional fireworks display, and also a theatre whose productions included the
suggestively named
Boarding School Romps. The building was let in 1752 to John Wesley as a chapel.
In Corporation Row, close by, were once the Mulberry Pleasure Gardens (1742 – ?). Their
proprietor, unusually,
did not charge for admission, presumably making his money from the sale of refreshments. Apart
from a
skittles alley, a pond, and shady walks, patrons could enjoy music, fireworks and
.illuminations.. Again the
place was popular mainly with tradesmen and artisans.
Sheila Miller explained that by the end of the 18th century the taste for pleasure gardens was
declining. In
Clerkenwell only New Tunbridge Wells ever attracted the upper classes, and they could afford to
travel to
provincial (or continental) spas to take the waters, or to the increasingly fashionable
seaside. In any case the
owners of the land occupied by these gardens (which only functioned in the summer months), so
close to
central London, could by then get a better return from building on it. Sheila knows her subject
thoroughly, and
brought it to life with contemporary quotes, extracts from John Rocque’s London map and the
many illustrations
she has collected. This was a most interesting and entertaining afternoon.
Judith Goodman
TRAFALGAR 200
Jane Smith The Story of Nelson’s Portsmouth Halsgrove, Tiverton 2005 ISBN 1 84114 476 2
Hardback
pp160, many illustrations £19.99
In a year which is seeing even more than the usual number of new books about Nelson (one
reviewer dealt
with eight in a single article recently) here is one which is different. Jane Smith, who has
recently joined
this Society, is primarily a social historian. She has looked at Nelson’s connection with
Portsmouth, and
at Portsmouth’s place in Nelson’s own story. Though Jane grew up in Mitcham and went to Mitcham
County (Grammar) School for Girls, she now lives in Southsea, and Portsmouth is part of her
family
background. With enthusiasm and scholarship she has produced a fascinating, if quirky, study of
the city.
By describing how the Portsmouth Nelson knew had evolved as it had, and then explaining how it
has
changed since, she manages to give us a pretty complete history of the place. (I was surprised
to learn, for
instance, that even in Nelson’s day Portsmouth was primarily still a military garrison town.)
Keyed into
the history of the port is the story of Nelson’s family background, of his life, particularly,
of course, the
naval side of it, and of his death. The last chapter looks at the Nelson monuments and other
reminders of
him to be seen in and around Portsmouth in 2005.
I have not yet read Colin White’s new collection of unpublished Nelson letters, but Jane Smith
has
reproduced the nearly 60 letters in the Nicolas edition which were written from Portsmouth, or
from its
anchorages of Spithead and St Helen’s (and at last I know just what and where they are),
letters which
span the 23 years from 1782 to1805. She makes it clear how important the place was in Nelson’s
career.
Not, by the way, that he liked it . .that horrid place. he called it in a letter to Emma
Hamilton.
If I have anything at all in the narrative to quibble about, and it is only a trifle, it is the
statement that Sir
William Hamilton’s death enabled Nelson and Emma to .live more freely as a couple.. On the
contrary,
they could no longer claim that a .pure friendship. alone was the bond. Nelson had to move out
at once,
until first his sister-in-law and then his niece could move in, as chaperon (not that anybody
was fooled!).
The text is lively and there are copious illustrations, from many sources, including plenty of
maps and
charts, prints, paintings and photographs (these latter often by the author). I was
particularly taken with
the exquisitely detailed pictures from the 1698 Survey of the Royal Dockyard. This was carried
out for
William III, and is now in the King’s Library at the British Library. No one lightly undertakes
.the trouble
of an index., as Byron put it, and that is a lack, but there is a really useful bibliography.
JG
MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY . BULLETIN 155 . SEPTEMBER 2005 . PAGE 5
VISIT TO APSLEY HOUSE AND THE WELLINGTON ARCH
Although only eight members booked for this event it proved most interesting, and those not
present missed a treat.
We were met at Apsley House by our guide who gave us a most informative tour of the house,
built by Robert
Adam between 1771 and 1778 for baron Apsley, who became the second earl of Bathurst. In 1807 it
was sold to
the marquess Wellesley, elder brother of the duke of Wellington, and he later sold it to his
more famous brother,
the duke. He set about improving it and extending it, with the help of the architect Benjamin
Dean Wyatt. The
house is the London home of the present duke and his family.
As you enter the hallway you are faced by the huge, nude statue of Napoleon, 11ft 4 inches
(3.45m) in height, by
Canova, apparently commissioned by Napoleon, who didn’t like it. It was presented to the duke
by George IV,
who had bought it from Louis XVIII.
Next we visited the dining-room containing the long mahogany table on which sits the 26ft
(7.9m) long centrepiece
of the Portuguese Service, made of silver and silver gilt. It represents Wellington’s victories
against the French
in the Peninsular wars and was a present from the Portuguese. The Piccadilly Drawing Room,
designed by
Robert Adam, was redecorated by the duke.
But the most significant room in the house is the Waterloo Gallery, designed in 1828 by
Benjamin Dean Wyatt
principally to provide a gallery for Wellington’s art collection. It is 90ft (27m) long and
could be used as a
ballroom or for entertaining. Its design is based on the Hall of Mirrors at Versailles, and, as
our guide showed us,
every window can be converted to a mirror. In total the rooms open to the public at Apsley
House contain around
200 paintings, including works by artists such as Sir Joshua Reynolds, Rubens, Caravaggio and
van Dyck.
After viewing the main rooms on show, which, in common with many grand houses of the time, are
all upstairs,
we came downstairs to view the Plate and China Room. This shows the gifts presented to the
first duke in honour
of his military achievements, from governments and leaders of countries aided by his campaigns.
Displayed here
is a priceless collection of porcelain and silver, many pieces specially commissioned, such as
the Wellington
Shield of 1822, portraying Wellington crowned by Victory and surrounded by ten scenes from his
career.
From here we left to visit Wellington Arch, where we were met by our new guide George, and were
glad of tea,
coffee and biscuits and a short rest. The Arch was built in 1825, near Apsley House, designed
by Decimus
Burton as a western entrance to London, as was the Temple Bar an eastern entrance. Both this
arch and Marble
Arch were built to commemorate Britain’s victories over Napoleonic France.
A large statue of the Duke of Wellington was placed on top of the arch in 1846, but it was
never very popular. In
1882, when surrounding roads were widened the arch was moved to its present site at the top of
Constitution
Hill, and the statue was removed to Aldershot. It was eventually replaced in 1912 with the
magnificent sculpture
of a quadriga (4-horse chariot) which we see today, designed by Adrian Jones.
More recently road traffic plans have changed again resulting in the Hyde Park Corner
roundabout and underpass.
In 1962 an airshaft was needed for the tunnel, so the arch was adapted for that purpose,
causing damage to the
structure. It had been in use as a police station, with 12 policemen stationed there, since
1831, one of the two
smallest police stations in London. However in 1999 the Arch came under the care of English
Heritage, and
major repairs have been carried out, with public access, lifts, walkways, displays, an
exhibition and a shop. It
opened to the public in 2001, having had £1m spent on it.
After viewing the exhibits we went up to the roof, from which we had excellent views to
Buckingham Palace in
one direction, and to Apsley House in the other. You also get a magnificent view of the many
and varied memorials
in the area, such as the Royal Artillery Memorial and the Commonwealth Memorial Gates.
Altogether this was a most successful and interesting visit, in which we were fortunate to have
excellent guides,
and a lovely sunny day.
Sheila Harris
TRAFALGAR 200
Look out for the attractive full-colour brochure Nelson’s Paradise Merton 2005 Events produced
by the
London Borough of Merton, with Heritage Lottery Fund support. A great variety of events are
listed,
with booking details. Available at libraries, Heritage Centre, Civic Centre etc.
Nelson Trail Information will be available in September.
MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY . BULLETIN 155 . SEPTEMBER 2005 . PAGE 6
SHAW’s CORNER AND HATFIELD HOUSE
A fine day, a full coach, a familiar driver (the cheerful and skilful Mick) and a free-flowing
M25 . the Kilsbys
had done it again. Another successful outing. Just over half our number came from the MHS, and
the rest were
members of Sanderstead and Selsdon WEA. A congenial mix.
Ayot St Lawrence is tucked away in a network of Hertfordshire’s narrow lanes. The house known
as Shaw’s
Corner was built in 1902 as a new rectory for the tiny village, but was available to lease four
years later. George
Bernard Shaw and his wife Charlotte were looking for a quiet retreat in the country where he
could write
undisturbed, and they took it at once. In 1920 they were able to buy it, for £6220. Oddly
enough its main appeal
was that neither of them liked it, and so neither would be tempted to spend on improvements
time that would be
better devoted to literature (GBS) or travelling (Charlotte). Indeed it is a rather unappealing
building externally,
but the rooms, if small, are sunny and pleasant, and the large garden is a charming mix of
lawn, trees and formal
and informal planting. There is a distant view across gentle countryside.
We were given a lively introductory talk by the enthusiastic young curator and were then free
to wander in house
and grounds.
Though the Shaws kept a flat in London, Ayot St Lawrence was their main residence. It was here
that admirers
from all over the world sought GBS out. We saw the small revolving hut in the garden, where he
liked to write,
and which enabled the housekeeper to say, with truth, that he was .out. to unwanted callers.
Shaw outlived Charlotte and arranged before his own death that the house should pass to the
National Trust. The
rapid transfer ensured that the house came to the Trust just as it was in its owner’s lifetime,
and it still retains this
personal character. The rooms are very much as they were, including his bedroom, where his
hairy dark brown
dressing-gown lies on the bed. Charlotte’s bedroom is now a small museum, where, as well as
photographs and
other memorabilia, there is a GBS puppet in a tweed suit and woollen stockings, and also the
bicycle off which
he so often fell. Some of his pre-printed postcards are on the wall . responses to requests for
information about
his views (vegetarianism, capital punishment .), for advice . or for money. Presumably he did
not sign these.
.Mr Shaw does not give autographs..
After a carvery lunch in the pretty village of Lemsford, we went on to Hatfield
House, the stupendous Jacobean (1611) house built by Robert Cecil, Earl of Salisbury,
who was chief minister to James I, and was the son of Lord Burghley, the great
statesman of the previous reign. A wing of the early Tudor palace, where Elizabeth
I spent her childhood, survives in the grounds. Despite the growth of Hatfield to a
sizeable town at its gate, and the railway station opposite, the house retains its dignity
unimpaired. Of red brick with stone, it is E-shaped, took five years to build, and cost
£10,000 for the structure and three times more for the decorations, furnishings and
landscape. The designer and clerk of works was Robert Lyminge, and there may
have been a small input from Inigo Jones.
In the immense Marble Hall, which is hung with tapestries and has a minstrels.
gallery, is the Ermine Portrait of Elizabeth I by Nicholas Hilliard, which shows an
ermine . symbol of purity . balancing on the cuff of the queen’s sleeve and gazing
up at her.
Round the corner, at the foot of the Grand Staircase is the Rainbow Portrait by Isaac Oliver.
The queen holds a
rainbow with her right hand, while on her left sleeve there is embroidered a large coiled snake
(wisdom?). She is
enfolded in a robe embroidered with eyes and ears, signifying that she knew all that went on in
her realm . which
she probably did.
The Long Gallery, largely unchanged, with its massive fireplaces, ornate panelling and gold
leaf ceiling, runs the
full width of the house. After that our route took us to the Winter Dining Room and the
library, both created in
the 1780s from bedchamber suites. The chapel is largely Victorian, but retains the original
Flemish stained glass.
The gardens are a mixture of formal and informal, with much recent work having been done to
recapture earlier
traditions, including a new Knot Garden in front of the Old Palace. Within some one-time farm
buildings a
pleasant café and a small model soldier museum have been created.
This was a varied and most enjoyable day. Many thanks to Ray and Pat for a good choice of
visits, for their
meticulous planning and for their efficient arrangements.
(I think, if I could choose one thing to take away with me from each house, it would be GBS’s
dressing-gown and
a rock crystal goblet from the Long Gallery!)
Judith Goodman
(Rectangle comment XPMUser
25/05/2017 00:46:36
blank)
Lord Burghley (father of
Robert Cecil) Riding his Mule
(Hatfield House)
MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY . BULLETIN 155 . SEPTEMBER 2005 . PAGE 7
200 YEARS AGO
SEPTEMBER TO DECEMBER 1805
NELSON AT MERTON
On 1 September 1805 Nelson knew for certain that he would be taking command for what all
expected would be
the climactic event of the war at sea. He told William Pitt, the Prime Minister, that he was
.ready now.. Final
decisions had still to be made at ministerial level, but, while waiting for these, Nelson had
much to do on the
domestic front at Merton Place, the much-loved home he shared with his lover Emma Hamilton.
With his gardener Francis Cribb he discussed plans for further improving the grounds, and he
gave Cribb money
for a christening robe for the baby his wife was expecting [see page 9]. He settled the
tradesmen’s accounts for the
work completed on the house, £1900 in all. The carpenter, bricklayer, plumber, mason, slater
and smith had been
waiting some time, and must have been relieved. He arranged with his friend and banker
Alexander Davison to
pay the architect Thomas Chawner for work already done on the house and for .what is ordered,
viz. the kitchen,
anteroom, and for altering the dining-room . The alteration will cost three times as much as if
it had been done
at first. However Chawner now knows all my plans and wishes ..
On the 5th he sent his luggage off to await him at Portsmouth.
He visited the Merton vicar Mr Lancaster’s school in Wimbledon, at what is now Eagle House, and
persuaded him
to give the boys a half-holiday. Thereafter the school was known as Nelson House Academy.
The William Nelsons were at Merton, as was Nelson’s sister Susannah Bolton and her family. They
were joined by
16-year-old George Matcham, son of the younger sister Catherine. George kept a laconic diary in
which he recorded
a grand visitor at this time: .HRH Duke of C[ambridge] din.d here. Like the King.. On another
day the entire
household dined at Morden Lodge with the hospitable Abraham Goldsmid and his family. Young
George did not
like the kosher food, and described the décor as .gaudy . but tasteless..
Nelson now knew that he was to be on board the Victory on the 14th. On the 12th he went to town
to say good-bye
to the Prince of Wales and to attend the Foreign Office. He was late home for dinner, where his
guests were
neighbours James Perry and his wife, from Wandlebank House, and his old friend Lord Minto. In a
letter to his
wife the latter wrote that Emma was in tears, unable to eat, and scarcely to drink, and half
swooning at the table.
On the 13th Nelson was off to the Admiralty for final orders, then home for dinner at 3.30 with
only the family,
followed by a quiet evening, and then, at 10.30, a post chaise ordered from the King’s Head
took him from his
.dear, dear Merton., as he wrote in his diary. He arrived in Portsmouth early the following
morning, where he was
greeted by Mr Lancaster, who had brought his own 14-year-old son Henry to join the Victory as a
volunteer 1st
class [see page 15]. Lancaster took a letter from Nelson back to Emma.
TRAFALGAR
Two weeks later, on 28 September, the Victory had joined the
British fleet blockading Cadiz, where the Franco-Spanish fleet
lay. Who knows how long the stalemate might have lasted?
But Napoleon goaded the French admiral Villeneuve into
embarking for Italy to support the French army there, and on
18 October the combined fleet . 33 ships of the line, five frigates
and two brigs . reluctantly put out from Cadiz to head for the
Mediterranean.
While Nelson’s fleet was smaller then he had hoped . only 27
ships of the line, his four frigates kept him well informed and
he made his plans accordingly. He divided his ships into two
columns. One, led by him in Victory, would attack the enemy
line in the centre, at their flagshipBucentaure. Admiral Cuthbert
Collingwood inRoyal Sovereign would lead the second column
and attack the rear. The intention was to disable half the enemy’s
fleet before the van could turn to help.
When Villeneuve saw the British fleet at dawn on the 21st he
caused his fleet to wear round to the shelter of Cadiz, off Cape
Trafalgar. He was not hopeful: after months of blockade his
men, who were in any case less well trained than Nelson’s,
were far from battle-ready. Collingwood engaged the Santa
Ana only shortly before the Victory was in action at close range
with the French Redoutable and Bucentaure and fighting
became general and fierce. Shortly after one o.clock Nelson
(Rectangle comment XPMUser
25/05/2017 00:46:59
blank)
The position of the two fleets at noon on 21 October 1805.
From O Warner, Trafalgar Batsford, London 1959
MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY . BULLETIN 155 . SEPTEMBER 2005 . PAGE 8
was wounded by a sniper from the
rigging of the Redoutable. He was
taken below and died some three hours
later. His devoted friend and flag-
captain Thomas Masterman Hardy
kissed him shortly before he died.
Nelson lived long enough to know that
the battle was won, and won decisively.
He had hoped to capture 20 enemy
ships, but was content with 15. The
effect of the win would be lasting.
RETURN
Immediately after the battle, which had
been fought in light winds, a gale blew
up, and it was not till 26 October that
Collingwood’s dispatch announcing
the victory and Nelson’s death could
be sent. Lieutenant John Lapenotiere
in the fast schooner HMS Pickle
reached Falmouth on 4 November and
London at 1am on the 6th. The news
was brought to Emma at Merton, and
she lay prostrate for hours in grief and
shock.
Meanwhile Nelson’s body had been placed in a large water cask filled up with brandy, and was
being brought back
to England. In the Downs, off Deal, it was dressed in uniform and place in a coffin made from
the mast of L.Orient,
the French ship which had blown up at the battle of the Nile. Encased in lead, and a second
wooden casket, it
continued its voyage, into the Thames, finally arriving at Greenwich in late December, to lie
in state.
A Note on Nelson’s Gardener
Nelson’s gardener at Merton Place had the name of Cribb. Canon J E Jagger, vicar of St Mary,
Merton, published
a booklet in 1926 which he called Lord Nelson’s Home and Life at Merton, and since then
Nelson’s biographers
have used this, together with Philip Rathbone’s Paradise Merton (1973) as their principal
sources for Nelson’s life
here. (I see that Christopher Hibbert in his 1994 biography refers to it as Nelson’s Love and
Life at Merton!) In this
text Jagger seems to have been the first to identify the gardener specifically as Thomas Cribb,
with a wife called
Ann. A well-known story goes that Nelson asked for the baby which Cribb’s wife was expecting
when the naval
hero was about to depart for Trafalgar to be baptised either Horatio or Emma. However, oddly,
Jagger did not
mention which the baby turned out to be. And if, as I finally did, one consults the Merton
parish register, one sees
that Thomas and Ann Cribb had seven children baptised at St Mary’s, including an infant
daughter who on 20
October 1805 was given the name, not of Emma, but Mary. That is a surprise . were Thomas and
Ann reluctant for
their daughter to be named after a notorious woman? Maybe, but the said woman was Thomas’s
employer. Or was
she?
I had noted a paragraph in the Surrey Independent for 12 January 1889 about the death at 95 of
James Hudson,
described as the son-in-law of Nelson’s gardener. Hudson is buried near the north wall of the
churchyard, with his
wife Maria . which is not one of the Cribb names in the parish register. It all remained a bit
of a mystery, which I
should have pursued. However, when a middle-aged man and woman unexpectedly rang my doorbell
one day and
introduced themselves as two descendants of James Hudson, all soon became clear. They gave me a
photocopy of
a supplement to the Merton Church Monthly for May 1889, which was called .A Short Sketch of the
Life of James
Hudson.. And this told me that Nelson’s gardener was not Thomas Cribb but Francis Cribb. And
when it occurred
to me to consult the parish register for Wimbledon I found that a daughter of Francis and
Hannah Cribb was
baptised at St Mary’s Wimbledon on 24 November 1805 and was given the name Emma. Canon Jagger
seems to
have assumed, quite reasonably, that the Cribbs, like their employers, attended Merton church.
But they may very
well have lived over the parish boundary, in Wimbledon, or may just have preferred to attend
the Wimbledon
church. Maria, who grew up to marry James Hudson, was baptised in May 1797, but her mother’s
name is given
as Anne . a mistake? Or was Francis married twice?
Incidentally, and sadly, Bill Rudd tells me that Francis Cribb, who is buried at Morden, ended
his days in the
workhouse. The name of Cribb lived on in the Merton Abbey area for many years as that of market
gardeners, and
a local roadway was at one time known, unofficially, as Cribb’s Alley. JG
Death of Lord Viscount Nelson. A print of 1813.
Blood gushes from the wound in Nelson’s left shoulder. He is shown wearinghis decorations, and
on the deck is his hat, which even bears the chelengk, aclockwork-operated diamond spray given
him by the Sultan of Turkey.
(Author’s collection)
MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY . BULLETIN 155 . SEPTEMBER 2005 . PAGE 9
.HATFEILD’s PARK . THE UNTOLD STORY’
Merton Historical Society member Sheila Miller and myself were delighted to make a visit on 16
July to
Morden Hall Park, to a wonderful day of reminiscences, exhibitions, performances and archival
film presentations
on life in the Park in the days of its last owner Gilliat Edward Hatfeild, who died in 1941 and
in his will left the
Park to the National Trust.
The Untold Story project is part of a three-year nationwide programme, and .Hatfeild’s Park. is
one of 18
projects which the National Trust have embarked on . challenging the traditional way of telling
stories about
National Trust historic homes and countryside. The project has been awarded a £375,000 Heritage
Lottery
Fund grant to work in partnership with youth and community organisations, to push the creative
boundaries of
interpretation at National Trust sites.
With the .Hatfeild’s Park. project Age Concern has been involved, and it has proved a great
opportunity for
older people to share their memories of living in Morden in the days of Mr Hatfeild. This
special Open Day was
part of Merton’s Festival for the Over-Fifties, organised by Age Concern, Merton. Also involved
in the dramatic
presentations were the New Wimbledon Youth Theatre. So there was great community involvement in
the
whole project.
When we arrived for the 12 o.clock performance we were divided into groups, and watched three
performances
in different areas of the Park. Firstly we saw .It Feels Just Like The Countryside., with three
people talking
about all the activities once enjoyed in the Park, like fishing, paddling, chasing the cows,
and watching the deer
being caught and killed. The participants were an actor, a National Trust employee and an older
Morden resident.
Then we moved over to the rose garden to see .Film Garden Party 1952., where a group of actors
and volunteers
acted out the wonderful garden parties that were held here in the late 1940s and the 1950s.
Morden residents
flocked there in their thousands to gaze at the stars, and get their autographs, and, if they
had a lucky programme,
maybe to speak to them. Finally we watched a presentation called .Mr Hatfeild’s Parties., when
a group of
children dressed in the clothes of the period acted out the wonderful times they had once a
year, when Mr
Hatfeild invited all the children of Morden to a tea party in his park. There were rides in
punts on the Wandle,
and a fairground, as well as a picnic tea in a marquee.
After some refreshments at the café we then returned to the Snuff Mill Centre, which is still
in the process of
restoration, with new toilets, kitchen and disabled access. In the newly restored downstairs
rooms there were
displays of photographs and memoirs of the people of Morden. There was also an interesting
collection of
framed photographs of inside Morden Hall, when it was a military hospital. Finally we watched a
series of
newsreels about the Film Star Parties run annually from 1947 to 1952 in the Park. Here we could
see all the
famous stars of the 40s, like Margaret Lockwood, Michael Wilding, Richard Attenborough and John
Mills,
surrounded by their adoring fans from Morden and its neighbourhood. There was also a very
amusing film
showing the building of the (then) new Morden cinema.
Altogether this was a very successful day. I understand the work collected will be kept as an
educational
resource for visitors and school groups. Also a monthly group meeting for older people will be
set up to share
memories, walk in the park, and make friends.
Anyone interested can ring Morden Hall Park on 020 8545 6850 or e-mail
lisa.green@nationaltrust.org.uk.
Sheila Harris
FROM MONTY’s POSTBAG
This time it was a telephone call, followed by letters, that Eric Montague received, from Brian
Bond of Essex,
with whom both he and Peter Hopkins have been in touch in the past about Arthur Bond of
Harland’s at Phipps
Bridge. During a visit to Australia this year Brian met a local historian who had interesting
information about
a Merton in New South Wales.
It appears that a Lieutenant William Ogilvie, who is said by some to have served with Nelson at
Trafalgar,
emigrated in 1825, with a free passage, to Australia. With a government grant of 2000 acres he
established a
homestead, which he called Merton, on the Hunter River. He was later able to purchase another
4000 acres at
five shillings an acre. The history of the place was typical of many early settlements . forced
convict labour,
imported contract workers from Germany (for the vineyard), intermittent lawlessness,
confrontations with
aborigines, Chinese labourers who disappeared to the goldfields and so on. Ogilvie and his wife
were said to
have been kindly and compassionate employers. Later the settlement declined, but it still
exists, though renamed
as Denman. It is still a wine-producing place. Denman is about 100km NNE of Sydney, the nearest
town being
Muswellbrook.
MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY . BULLETIN 155 . SEPTEMBER 2005 . PAGE 10
Brian Bond wondered if Ogilvie hailed from our Merton, or did he name his estate after Nelson’s
out of
sentiment? Did he really serve at Trafalgar? Peter Hopkins has produced some answers. In 1819
at the manorial
court at Merton William Payne was granted licence to demise and let Merton Farm to William
Ogilvie .of
Merton., Lieutenant in the Royal Navy. The land tax records confirm that Ogilvie held Merton
Farm in 182024,
after which he no longer appears. Merton Farm house survives as the misleadingly named .Manor
House.
at 120 Kingston Road.
Though Ogilvie named his Australian estate after his English one, the possibility remains that
he came to
Merton in the first place because of its association with Nelson. I believe that there is a new
CD listing everyone
who served at Trafalgar, and there may also be a useful website.
JG
A VISIT TO MIDDLETON-ON-SEA
On a hot and sunny day in late May seven Committee members
and one vice-president of the Society took the train to Barnham
and thence taxis to Middleton, or, more precisely, to Elmer Beach
Estate, on a visit to another Committee member, Eric Montague.
Here, in a narrow private road that leads only to the shore, and
within a pebble’s throw of the beach, stands Elmer Cottage
(otherwise Montague’s Mansion). Monty has known Middleton
since he was a boy, and has lost count of the number of holidays
he has spent there. In time the family bought one of the typical
holiday cottages that had sprung up at the Elmer end, and it was
that cottage that Monty has now replaced by a house of his own
(brilliant) design, one suited to year-round occupation,
entertaining guests, doing research, and sitting in the sun.
Monty, of course, belongs to local history societies in the area,
and to Sussex Archaeological Society, so we knew we were in
capable hands when he led us on a stroll around Middleton. The
name .Elmer. means .eel pool.. Elmer was a tithing of Arundel
within Middleton parish, which is only half the size it once was,
the rest having been lost to the sea. The medieval church finally
collapsed and was washed away in 1838, to be replaced ten years
later by the present one, sited well inland.
At the end of Monty’s road, from where we could see the Isle of Wight in the distance, a
fragment of the
Common Sea Bank, built shortly before the first World War, survives, with tamarisk growing on
it. Recently
several .islands. of rocks have been created close to the shore to break up the action of the
current . with some
success. Spits of sand now extend out towards the artificial islands, and the effects are being
monitored.
Monty pointed out holiday houses dating from the early 20th century, some incorporating old
railway carriages,
some hardly changed, though smartly kept, others with extensions and .improvements., some so
embellished as
to be unrecognisable as originals. When they were first built there had been little in the way
of services available,
but soon it was a thriving, if mainly seasonal community. At one time in Elmer there was a
proper shopping
centre with butcher, fishmonger, off-licence general stores and so on. But now, though many
houses these days
are lived in all year round, there is just a post office/shop, a couple of takeaways and a pub.
There is however a
bus service to Bognor.
The present layout of Middleton can be related to old field
boundaries as shown on early maps, such as one made in 1606 for
lord of the manor John Spencer, one-time Lord Mayor of London.
Some field paths survive between the houses, and here and there
are some old buildings. One of these is the picturesque Ancton
House, which Monty suggests is mainly 16th century, with an 18thcentury
wing. Nearby are field walls of flint, some incorporating
Tudor bricks, and a hedge estimated to be 1000 years old.
We enjoyed our day by the sea and the sights of Middleton and
are grateful to Monty for his kind welcome and our interesting tour. JG
Elmer Cottage (photograph by Sheila Harris)
Ancton House Hotel, Middleton-on-Sea (postcard)
MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY . BULLETIN 155 . SEPTEMBER 2005 . PAGE 11
It is more than time that the Bulletin celebrated a great local sporting tradition. So, as the
2005 season
comes to an end, here is a small anthology devoted to cricket at Mitcham.
MITCHAM CRICKET I
One of member Cyril Maidment’s most prized possessions is an autographed copy of the Mitcham
Cricket Club
Year Book for 1946. His uncle bought it for him when it was auctioned after a match at the Oval
between .Old
England. and Surrey. Small Cyril was thrilled (the thrill has not worn off) to have the
signatures of so many
cricketing giants.
This was the first Year Book to appear after six years of war. The names of five members who
died serving in
the RAF are recorded, and there are two accounts of playing cricket overseas in the services.
There are articles
for and against the possible formation of a .London League.. Tom Francis contributed a light-
hearted piece
about cricket bats, and Burn Bullock a few comic stories. In the list for the season the First
Eleven had fixtures
against teams representing Public Schools, Metropolitan Police and Surrey itself, while the
humble Wednesday
Eleven tackled teams from the Daily Sketch and the News of the World, and also Croydon
Pawnbrokers (did
they use only pledged equipment?).
Advertisers include the Wandsworth & District Gas Company, The Wilson Hospital (.Great Scoring
in 1945! .
Admissions 1,710 etc..), Ruff’s Repairs (.Established 1878.), Mitcham Model Laundry and Tom
Francis’s
London House (.Drapery . Shoes . Outfits . Ironmongery.). Also in the book is a much reduced
version of
Lucien Davis’s picture reproduced opposite.
The signatures
Frank Woolley
Nigel Bennett (Surrey captain)
Percy Fender
R J Gregory
E R T Holmes
T H Barling
M J C Allom
Stan Squires
Tich Freeman
J F Parker
Herbert Sutcliffe
Eddie Watts
Maurice Tate
A J McIntyre
E W J Brooks
G S Mobey
Douglas Jardine
T G Pierpoint
G A R Lock
G J Whittaker
Hobbs and
Andy Sandham
Strudwick were
Eric Bedser
the umpires
Alec Bedser
MITCHAM CRICKET II
The picture at the top of page 13 appeared in Cricket, a volume in the Badminton Library of
Sports and Pastimes,
which was written by A G Steel and the Hon. R H Lyttelton and published by Longman, London, in
1904. The
artist was Lucien Davis, and the drawing probably dates from the publication year, as it is one
of a number by
the same artist in the book. Note that the pavilion has not yet been built. Centrally, in the
distance, is the King’s
Head, now the Burn Bullock, and to the right is the White Hart. The elegant equestrians must be
from one of
Mitcham’s .big houses.. I am told that the batsmen appear to have turned for the second run
after a shot to deep
extra cover, which a fieldsman is running to retrieve.
MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY . BULLETIN 155 . SEPTEMBER 2005 . PAGE 12
(Rectangle comment XPMUser
25/05/2017 00:48:12
blank)
MITCHAM CRICKET III
The poem below was reproduced 30 years ago in the Bourne Society Bulletin No.92 in a
contribution by Roger
Packham. I recently wrote to Mr Packham asking if he had more information about it, and in his
reply he wrote:
.The poem appears in the cricket magazine Cricket . A Weekly Record of the Game for 30 March
1905, page 36,
and was contributed by F S Ashley-Cooper, who was a highly respected cricket historian.
.Ashley-Cooper wrote: .. the following fragment, owing to the fact that it was not issued in
separate form,
will probably prove unfamiliar to the majority of cricket enthusiasts .. and then gives the
title of the poem and
the poem itself. He then writes:
..About 1790, as indeed for many years both before and after, Mitcham was probably the
strongest cricketing
village in Surrey. For quite 200 years Mitcham has proved one of the strongholds of the game,
and in 1810
possessed such a number of fine players that it furnished five members of the Surrey team which
played England
that year at Lord’s. Coulsdon, although hardly famous cricketally[sic], has, nevertheless, a
certain fascination
for students of the game, for an old newspaper remarks: .The first match with three stumps and
two balls took
place on the Burway Ground, at Chertsey, in the match Chertsey v Coulsdon, played September 6th
1776…
Mr Packham adds that the poem has been included in a recently published anthology of cricket
poems collected
by David Rayvern Allen. He has kindly allowed it to appear in our Bulletin.
THE CRICKETING MUSE
On the second cricket match between Mitcham and Coulsdon,
played at Smitham Bottom, September 21st and 22nd 1791
1.
Mitcham! Well done, my boys, a second time,
Thy glory now must still extend my rhyme.
Now Coulsdon is by Mitcham beat once more,
And now she glories as she did once more,
Your triumph, neighbours, now it is complete,
Coulsdon was fairly by eight wickets beat.
2.
Tho. Coulsdon first got five times ten,
It was exceeded by the Mitcham men,
Lads of Mitcham, the most gallant .leven,
Fairly headed them by five times seven.
The Coulsdon next they just got forty-four,
And all the .leven they could get no more.
3.
The Mitcham men they little had to do,
The work was fairly done in wickets two;
Four Mitcham lads advanced upon the plain,
And wielded not the cricket bat in vain;
Tho. forty-four Coulsdon had gained complete,
Soon Mitcham gained forty-five to beat.
4.
Sanders, the Tipstaff, Hinckley, all gained fame,
And as for Mitcham lads they closed the game,
.Twas Hinckley’s lot to strike the final blow,
To gain the notch that proved the overthrow;
They fairly showed how Mitcham men could play,
And gallantly they early closed the day.
MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY . BULLETIN 155 . SEPTEMBER 2005 . PAGE 13
LOCAL HISTORY WORKSHOPS
Friday 13 May 2005. Seven present. Judith Goodman in the chair.
©
Sheila Harris had been given a copy of the annual report of West Norwood Athenaeum, an
antiquarian and
historical society founded three-quarters of a century before this one. They have a programme
of visits
throughout the year. Judith Goodman remarked that John Innes’s architect at Merton Park, H G
Quartermain,
had been an active member and was given a handsome obituary in their Record of 1904.
©
Cyril Maidment had been gathering information on Irish monasteries from the internet.
Mellifont, county
Louth, was the first Irish Cistercian foundation, in 1142, a daughter house of Clairvaux. A
modular system had
been used in the layout, but the method was not so simple or so accurate as that used at Merton
18 years earlier.
Cyril had been in correspondence with Robert Whytehead of the London Archaeological Forum about
the
limits of the scheduled ancient monument area of Merton priory. He wished to know if the sites
of recent
excavations were included. The matter had been referred to English Heritage, but it was agreed
that this
Society would also raise the matter in separate correspondence. [The Gatehouse site, tile kiln,
monastic
mill, medieval buildings nearby, fish ponds, drains are all outside the scheduled area, not
forgetting the
Abbey House site. . LG]
Cyril had used his expertise to amalgamate pictures of adjoining buildings in the High Street,
Merton.
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15
Albert E Reed & Co. Samuel Baylis William Morris Col. F.A. Wellesley
Paper Mills Iron Works & Co. Merton Abbey Gate House
Little was known of the ironworks of Samuel Bayliss, immediately to the east of the Morris
works, but a
similar illustration appears in Miss Jowett’s 1951 book (plate 32), where it is described as
the shoeing forge.
It shows a massive wooden horseshoe (upside down) over the front door.
©
Madeline Healey, recalling VE Day on 8 May 60 years ago, had brought along some photographs of
celebration parties of that time. [One was reproduced in Bulletin No.154. . Ed.]
©
Peter Hopkins showed print-outs of microfilms of the court rolls of Morden for 1377-86 obtained
from the
British Library. Members resisted reading the Latin text.
He had discovered in Surrey Archaeological Collections vol XII (1895) a reference to a Richard
Sampson
who had married a daughter of Thomas Garth of Morden.
©
Judith Goodman had been asked by a correspondent in Western Australia what was known here about
a
Joseph Talbot Hobbs who went to Merton Boys. School in the 1870s. Fortunately the school log-
books are
held by the John Innes Society (transcripts are at Surrey History Centre) and she had read
them, and
remembered Hobbs. name. He emigrated to Australia, where he became both a soldier and an
architect.
When he visited this country in 1897 as part of the Western Australian guard of honour at Queen
Victoria’s
Diamond Jubilee, he called at Merton to see again the school and headmaster he remembered . and
his visit
is recorded in the log-book. Hobbs later became a general.
Judith had brought along two recent purchases. One was the Surrey Archaeological Society’s
publication
Stained Glass in Surrey Churches (1930), and the other was the parish register of Wimbledon to
1812 (pub.
1924). This latter was the copy once owned by William Myson, who had been Wimbledon Borough
Librarian,
and it contained many of Myson’s notes interleaved.
Lionel Green
MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY . BULLETIN 155 . SEPTEMBER 2005 . PAGE 14
Friday 1 July 2005. Eight present. Lionel Green in the chair.
©
Sheila Harris drew our attention to a special event at Morden Hall Park on Saturday 16 July
[see page 10].
©
Madeline Healey was looking at the Chesterman family, in particular Widow Chesterman, who is in
her
family tree, and John Chesterman, of Mitcham Mill, who figures in Eric Montague’s Mitcham
Bridge ..
©
Sue Mansell had found a report in The Times of a study of many remains of religious members of
three
ancient foundations, including Merton priory, to be very interesting. In particular, there was
little evidence
of an abstemious life!
©
Peter Hopkins referred to the June Journal (Vol.28 No.2) of East Surrey Family History Society,
which
carried two articles of local interest . one concerned people associated with the Littler works
at Merton
Abbey and the Littler home, Abbey House, and the other was about the violent death of a Richard
Batter in
Wimbledon in 1854. There was also a request for information about William Snelling, who worked
at a
calico print-works at Merton Abbey from 1785 to 1825.
He advised that a recent acquisition at the Surrey History Centre was a 1942 survey of Morden .
geographical,
historical, statistical and social . compiled by IV Form pupils at Central Road Girls. School,
especially
relating to the St Helier Estate. Its accession No. is 7686. Other recent SHC acquisitions of
local interest are:
7601 Property in Wimbledon and Frensham: deeds 1867-74
7627 Railways at Wimbledon and Merton: plans, photographs, specifications and financial
estimates,
1881-1927
7640 Wimbledon County School for Girls: school photos 1922 and 1928
7665 Wimbledon High School: school magazines 1920-1962, and three photograph albums 1920s-1940s
©
Judith Goodman spoke of two young Merton people who became famous. Henry Lancaster, son of the
Revd Thomas Lancaster, friend of Nelson and vicar of Merton, was born on 12 May 1791. He served
on
HMS Victory at Trafalgar as a volunteer first class (the lowest rung of the midshipman ladder).
He was
promoted lieutenant in 1813, and his final rank was commander. He died in 1862.
She had learned more about Sir Joseph John Talbot Hobbs (1864-1938) [see workshop report
above]. Her
correspondent in Australia has embarked on a PhD thesis on Hobbs, who became a prominent
architect in
Perth, Western Australia, and also survived Gallipoli, where he was a key figure in the
Australian army. He
designed most of the first World War Australian war memorials in France. Hobbs attended Merton
School
from the age of seven until he was almost 15.
©
Bill Rudd spoke of the Wandle Valley Festival, held on 12 June, and the attractions prepared by
MoLAS,
the Heritage Centre and others, in the Chapter House. He was shocked by the intense development
of every
inch of the site.
He also bemoaned the shabby treatment of the local post offices (the ones that survive, that
is). As a matter
of interest, he said, the new Morden post office would not be far from the original one.
©
Cyril Maidment had brought two photographs of the VE Day party in Marlborough Road, Colliers
Wood.
He also showed a copy of the Mitcham Cricket Club 1946 Year Book, which had been autographed by
both
teams at the Old England versus Surrey match on 23 May 1946 [see page 13].
He referred to a dig at Nos 1-11 Colliers Wood High Street [see page 16], where Roman pottery
sherds had
been found. No one present had known about this.
He had made a drawing to help people judge just how big Merton priory church was, by comparing
it with
the parish church.
He had also made a composite print of the Nelson estate in 1801, and the Merton Abbey Gate
House estate
in 1805.
©
Lionel Green had prepared a draft .Outline History of Merton and its Parish Church. to replace
the old guide.
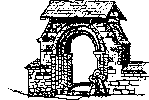
He showed an interesting photograph, P1018 in the Wimbledon Society Museum collection, which
shows in
detail the foundations of the beautiful Norman arch that was transferred from the .prior’s
house. to Merton
parish church.
He also spoke about the wonderful retable on display in Room 19 at the National Gallery.
Cyril Maidment
Dates of next workshops: Fridays 28 October and 9 December at 7.30pm at Wandle Industrial
Museum.
All are welcome
MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY . BULLETIN 155 . SEPTEMBER 2005 . PAGE 15
55th ANNUAL GENERAL MEETING
SNUFF MILL ENVIRONMENTAL CENTRE, MORDEN HALL PARK
SATURDAY 5 NOVEMBER 2005 at 2.30 pm
AGENDA
1 Chairman’s welcome. Apologies for absence
2 Minutes of the 54th AGM held on 6 November 2004
3 Matters arising from the Minutes
4 Chairman’s Report
5 Membership Secretary’s Report
6 Treasurer’s Report: reception and approval of the financial statement for the year 2004-05,
copies of
which will be available at the meeting
7 Election of Officers for the coming year
a) Chairman
b) Vice Chairman
c) Hon. Secretary
d) Hon. Treasurer
Appointment of the Hon. Examiner for the coming year
8 Election of a Committee for the coming year
9 Motions of which due notice has been given
10 Any other business
At the conclusion of the business part of the Meeting there will be a talk by Desmond Bazley on
.Gunpowder, Treason and Plot..
NOMINATIONS for Officers and Committee members should reach the Hon. Secretary 14 days before
the
AGM, though additional nominations may be received at the AGM, with the consent of members.
MOTIONS for the AGM must be sent to the Hon. Secretary in writing at least 14 days before the
meeting.
Please bring this copy of the Agenda with you to the AGM.
Our new MEMBERSHIP SECRETARY wishes to remind members that subscriptions are due on 1 October.
The current rates are:
Single member £7
Additional member in same household £3
Student member £1
A renewal form is enclosed with this Bulletin. Please complete it and return it with your
subscription to the
Membership Secretary, or in person at a meeting. Members who have already arranged to pay their
subscriptions
by Banker’s StandingOrder should ignore this renewal form.
RECENT ARCHAEOLOGY REPORTS
From the most recent English Heritage Quarterly Review (GLAAS):
1-11 High Street, Colliers Wood SW19
Excavation by MoLAS. Trenches on the western part of the site revealed a Roman ditch aligned NE
to SW
following the line of the route of Stane Street. To the west of the ditch possible evidence of
the construction
of the Roman road was observed. Evidence of the possible route of the River Graveney was also
revealed in
the NW part of the site.
Ricards Lodge School, Lake Road SW19
During a watching brief by AOL Archaeology in connection with the construction of synthetic
pitches a
tunnel running NE to SW and a large rectangular structure were observed. The rectangular
structure is probably
the robber cut and demolished material from Marlborough House, which burnt down and was
demolished in
1785. The tunnel was contemporary with the house and linked the servants. quarters with the
house.
Letters and contributions for the Bulletin should be sent to the Hon. Editor. The views
expressed in this
Bulletin are those of the contributors concerned and not necessarily those of the Society or
its Officers.
Printed by Peter Hopkins
MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY . BULLETIN 155 . SEPTEMBER 2005 . PAGE 16
 MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY
MERTON HISTORICAL SOCIETY 